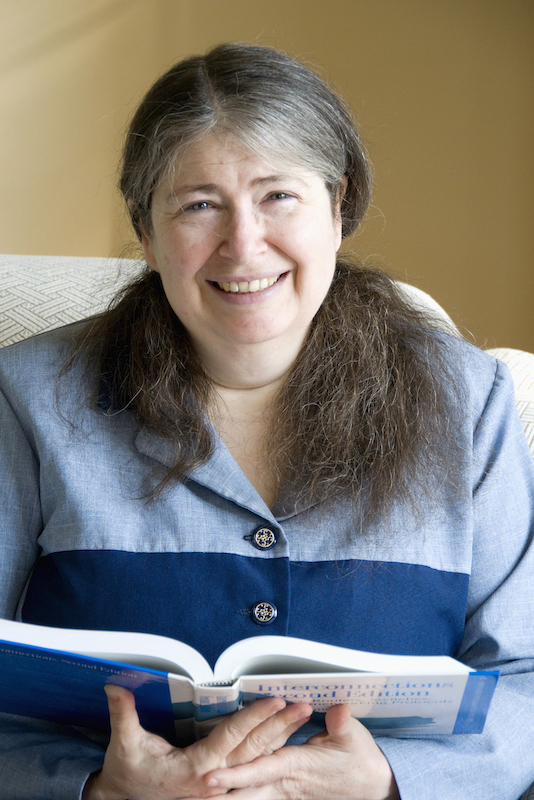
You want to beleive how great this woman was implement Spanning Tree algorithm. Often referred to as the Mother of the Internet, Perlman is a software designer and network engineer who is most famous for her invention of the spanning-tree protocol. Perlman, who developed spanning-tree while working for Digital Equipment Corp, holds a Bachelor’s and Master’s in Mathematics and a Ph.D in Computer Science from MIT. So, you know, girl’s got mad skills. Spanning-tree is a network protocol that ensures a loop-free topology for any bridged Ethernet local area network -which is fundamental to the operation of network bridges. Perlman is also a heavy hitter in other areas – most notably network design and standardization such as link-state protocols – including TRILL which she invented to correct the failings of spanning-tree. Perlman has also been called a pioneer in teaching young children computer programming for developing TORTIS, a version of the educational robotics language, LOGO. Currently employed by Intel, Perlman holds more than 50 patents from Sun alone, and is the author of a textbook on networking, and a co-author of a textbook of network security.

Goals
- Create a concept network based on number of nodes and edges
*The network can be thought of as a matrix of integers, which specify bridge IDs
*Output the diameter of concept graph since it’s important to know if Spanning Tree algorithm gets executed completely to make sure that diverse cost among bridges exists to root.
*Output message if the current state of randomly generated graph is a tree or not. *Output message if the generated graph is a single connected component. - Use Bron Kerbosch Clique finder to find cliques in the network.
- Create a LAN segment for each clique
- Create a bridge for each node
- Ensure each bridge is connected to at least two LAN segments.
- Run each single LAN Segment object and Bridge object in different threads.
Approach
For each Bridge thread we have the following algorithm. 1. Each bridge advertises its ID as root ID to all neighbors. 2. Each bridge listens for all root advertisement frames from neighbors. If the root ID of neighbor is less than its own ID, it accepts the neighbor’s ID and keep advertising it as new root ID until the specified timeout is reached. 3. Root bridge marks all of its ports as DP. 4. Once root bridge elected. Every bridge advertises its cost to reach root bridge to its neighbors. Each bridge marks the port with lowest cost to root bridge as RP port. 5. Every bridge advertises DP advertisements to neighbor bridges. The bridge with lowest cost to bridge marks its port to LAN Segment as DP port and the other one just block the ports. a. If a bridge didn’t receive any DP advertisements from neighbor LAN Segments, it means that there is no other LAN Segment on other side of bridge so it marks the port as DP. b. If two bridges have the same cost to root, they use their port ID as a tiebreaker. Simply the one with lowest port ID (MAC Address) wins the competition.
For every LAN Segment object, a bridge simply forwards every frame it receives to all other ports.
Once bridges are done, they report status of all of their ports as either “BLOCKED”, “RP” or “DP”
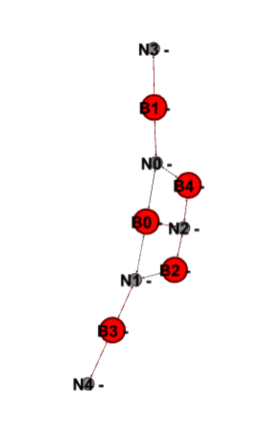
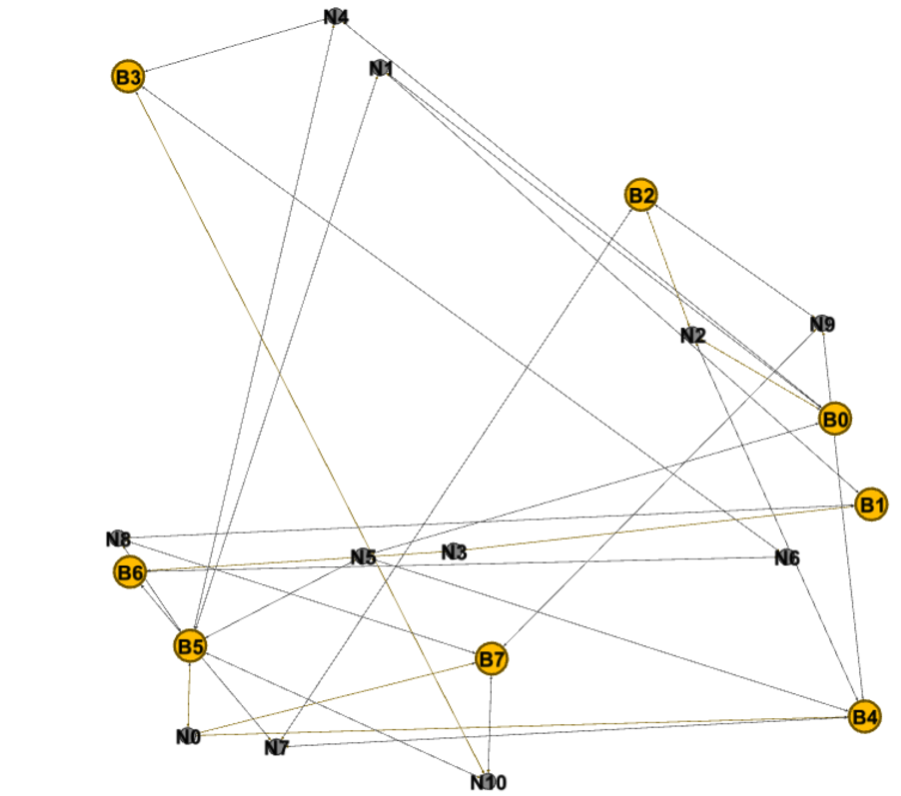
Design and Method:
- Used density as a probability factor to construct a concept network of bridges.
- Once concept network generated, extracted cliques to make LAN Segments. Just to make LAN Segments look more realistic and having LAN Segments with degree more than two.
- Based on concept network generated created network based on simulation objects.
- Ran all bridges and LAN Segments in distributed fashion. Used random numbers to make sure threads are desynchronized, just like real world.
- On bridge object implemented simple sequential state machine to keep track of the state of bridge.
Assumptions
Bridges can interconnect by shared medium namely networks. Hence more than 2 bridges can participate in Layer-2 by being interconnected through the same network. Therefore network structure forms a bipartite graph of two classes of nodes, bridges and networks where minimum degree for bridges and networks are two and one.

